How to Check if a URL is Safe for Online Transactions
In today’s digital age, online transactions have become a fundamental part of our daily lives. Whether you’re purchasing a new product, paying for a service, or simply managing your bank account, it’s important to ensure that the website you’re interacting with is secure. Cybercriminals are increasingly using sophisticated methods to create fake websites designed to steal your sensitive information, such as credit card details and personal credentials.
So, how do you know if a URL is safe before making any online transactions? In this article, we will guide you through a series of simple checks and precautions you can take to protect yourself while shopping or managing your finances online.
Understanding the Importance of a Safe URL
Before diving into the checks, it’s important to understand why a URL’s safety matters in online transactions. A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is essentially the address of a website. When it’s unsafe, it could be a fraudulent site designed to look like the one you intend to visit, aiming to steal your personal information. Safe URLs, on the other hand, ensure your data is encrypted and that you’re interacting with legitimate services.
Unsafe URLs may display subtle signs like incorrect spelling or unfamiliar domain names. These seemingly minor clues can indicate that you might be dealing with a phishing website or a malware-ridden site.
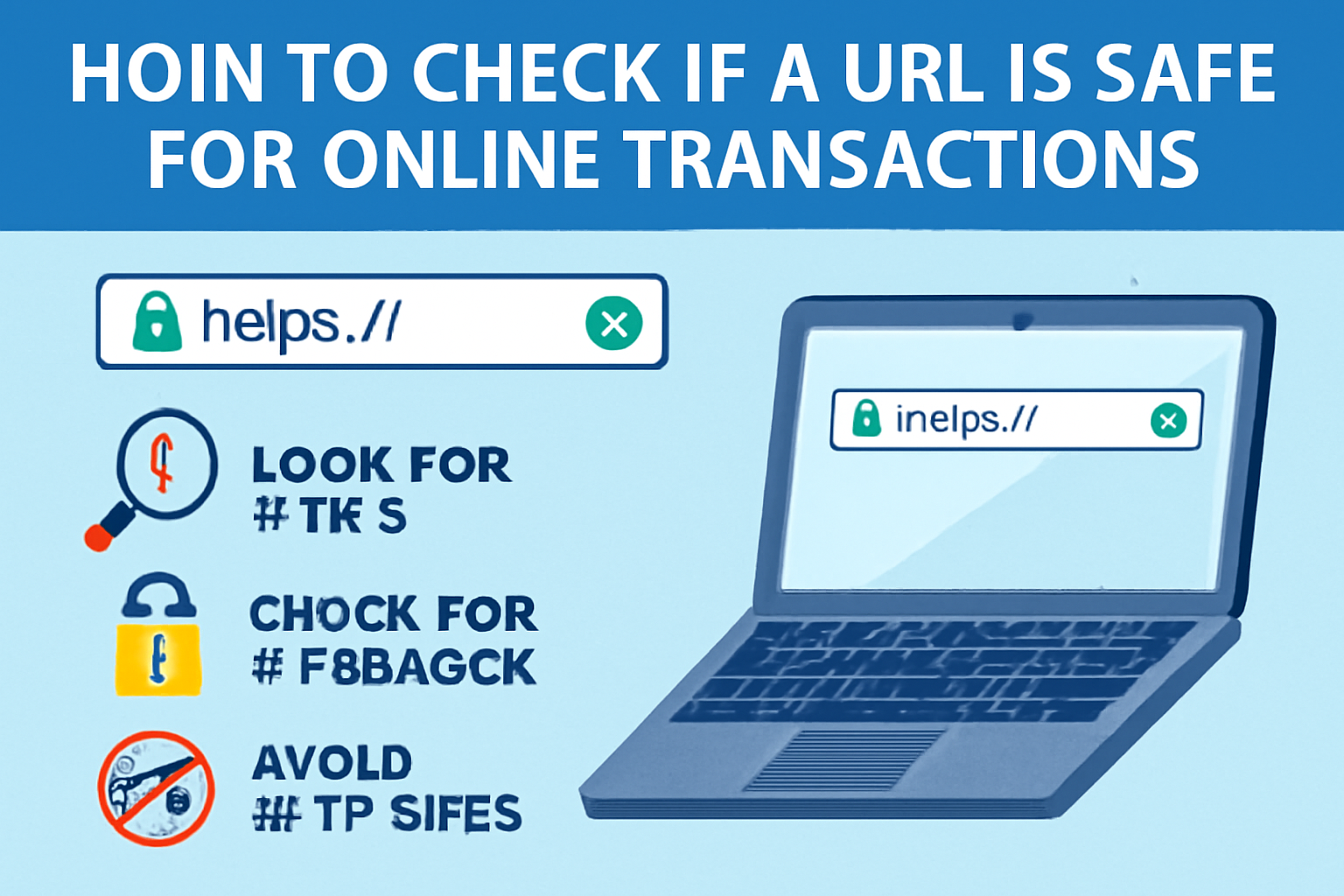
1. Look for HTTPS in the URL
One of the first things to check when you visit a website is whether the URL starts with “HTTPS” (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure). The “S” at the end of HTTPS signifies that the website is using an encrypted connection, which means any data transmitted, such as passwords or credit card details, is secure.
Without HTTPS, your connection is not encrypted, and your data can potentially be intercepted by malicious actors. Always ensure that a website you intend to make an online transaction with has HTTPS, particularly when entering sensitive details like credit card information or personal identification.
2. Verify the Website’s Domain Name
A common trick that cybercriminals use to create fake websites is to replicate the domain name of a legitimate site but with slight alterations. For example, they might use a similar-looking domain name or swap characters that look almost identical. This tactic is known as “typosquatting” or “URL spoofing.”
To avoid falling for this trick, always verify the domain name carefully. For instance, if you’re visiting a shopping website, check that the domain name exactly matches the official website you’re familiar with.
3. Check for a Padlock Icon
Another sign of a secure website is the padlock icon in the address bar. If you see a padlock before the URL, it means the website is using a secure SSL certificate to protect data exchange. This is especially important when making online transactions, as it guarantees that the information you provide is encrypted and sent securely to the website’s server.
If there’s no padlock icon, or if it has a warning symbol, it may be a red flag that the website isn’t secure.
4. Inspect the Website for SSL Certification
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) is a security technology that encrypts the connection between your browser and the website. SSL certification is crucial for websites that require sensitive transactions, like online shopping or banking.
You can check if a website has an SSL certificate by clicking on the padlock icon in the URL bar. A certified website will show a message confirming that the connection is secure. If the SSL certificate is missing or invalid, avoid making transactions on that site.
5. Use a Website Safety Checker scan url
A quick and effective way to check if a website is safe is by using a URL safety checker. These tools analyze the website’s URL and identify any potential risks associated with it, such as phishing scams or malware.
For example, you can scan url using a reputable online tool to determine whether the site is safe to visit or make transactions. These services check if the site is part of known phishing schemes or if it has any security vulnerabilities.
6. Check for Suspicious Pop-ups or Ads
If a website is bombarded with pop-up ads, it’s a cause for concern. A legitimate website typically does not overwhelm users with excessive ads. A secure, reputable website will have clean, well-designed pages with minimal interruptions.
Pop-up ads often come from malicious websites or online scammers who attempt to get your personal information or redirect you to malicious sites. If you notice an excessive amount of pop-ups while browsing, it’s best to leave the site immediately.
7. Look for Contact Information and Customer Support
A legitimate website will always provide clear and accessible contact information, including a physical address, customer service phone number, and email address. Scammers usually avoid providing legitimate contact details because it makes it easier for customers to track them down.
Before entering any payment details, take a moment to check if the website provides valid and professional customer support options. Legitimate businesses typically offer multiple ways to contact them, whether it’s through a help center, live chat, or a customer support hotline.
8. Pay Attention to Website Design and Content
A professional-looking website is usually a good indicator of legitimacy. However, even legitimate websites can sometimes be poorly designed or outdated. Pay attention to details like spelling errors, broken links, and low-quality images. These issues can indicate that the website is either poorly maintained or a fake site created to scam unsuspecting users.
Also, be cautious if the website asks for too much personal information. Reputable websites should only request necessary details. For example, asking for your social security number or excessive personal data can be a sign of a scam.
9. Avoid Clicking on Suspicious Links in Emails or Text Messages
Phishing attacks often involve fraudulent emails or text messages that contain links to fake websites. These messages may appear to be from legitimate businesses, urging you to click on a link and make a purchase or verify your account.
It’s important to always double-check the URL in these messages, as the links might direct you to a website designed to steal your information. Instead of clicking on links, visit the official website directly by typing the URL into your browser.
10. Use Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an additional layer of security to your online accounts. Even if a hacker manages to obtain your login credentials, they won’t be able to access your account without the second factor—usually a code sent to your phone or email.
When engaging in sensitive online transactions, especially on banking or shopping websites, enable 2FA to further protect your account and personal information.
11. Check for Website Reviews and Reputation
Before entering payment details on a website, take a moment to check the reviews and reputation of the website. You can search for online reviews, testimonials, and forums where users discuss their experiences with the website.
If the website has numerous negative reviews or no reviews at all, proceed with caution. Established businesses and e-commerce sites usually have plenty of feedback from users, so a lack of it may signal that the site is unreliable or fraudulent.
12. Trust Your Instincts
Sometimes, your gut feeling can be the best indicator of whether a website is safe. If something feels off about the website, or if you’re not sure about the URL, it’s better to be cautious and avoid making transactions on that site.
Phishing websites and fraudulent sites are designed to look as legitimate as possible, but often there’s something about them that just doesn’t seem right. Trust your instincts, and if you’re unsure, find an alternative website to make your purchase or complete your transaction.
13. Monitor Your Bank Statements Regularly
After completing an online transaction, it’s wise to monitor your bank statements regularly for any unauthorized transactions. If you notice anything suspicious, contact your bank or payment provider immediately.
Even if you’ve taken all the precautions, fraud can still happen. Keeping a close eye on your financial accounts will help you detect any unusual activity quickly.
14. Keep Your Software and Browser Up to Date
Regularly updating your browser, operating system, and security software is essential for safe online transactions. These updates often include security patches that help protect against new types of online threats.
Ensure your browser and antivirus software are up to date to better protect yourself from potential cyber threats when browsing and making online purchases.
15. Consider Using Virtual Payment Methods
If you’re especially concerned about the safety of online transactions, consider using virtual payment methods like digital wallets or prepaid cards. These options provide an extra layer of security by limiting the amount of sensitive information shared during transactions.
Many digital wallets use encryption and two-factor authentication to protect your data, offering peace of mind when making purchases online.
Conclusion
In conclusion, being vigilant and taking a few extra steps to verify the safety of a website before making an online transaction can go a long way in protecting your personal information and financial security. By checking for HTTPS, ensuring the domain name is legitimate, using a URL safety checker like scan url, and applying common sense, you can shop and perform online transactions with confidence.
Don’t let the convenience of online shopping lead to careless decisions—take the time to verify the safety of each website you interact with, and always prioritize your security.
For more information on URL safety, visit https://phishs.com/.